Look around at everyday items—water bottles, shampoo containers, automotive fuel tanks, and countless other hollow plastic objects. These ubiquitous products are most likely manufactured through blow molding, a specialized and fascinating manufacturing process that shapes modern life in ways most people never realize.
What is Blow Molding?
Blow molding operates on principles similar to traditional glassblowing, using controlled air pressure to inflate heated plastic material inside precise molds. The blow molding process begins with a soft, hot plastic parison (a tube-like piece) that gets inflated until it conforms to the mold’s interior shape, creating hollow objects with consistent wall thickness and dimensional accuracy.
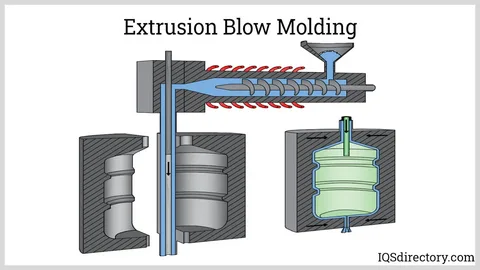
Extrusion Blow Molding
Extrusion blow molding represents the most widespread variant of this manufacturing process. In extrusion blow molding, a continuous parison is extruded downward, a split mold closes around it, and compressed air inflates the material to form the final shape. This blow molding technique proves ideal for high-volume production of bottles, containers, and other hollow products requiring consistent quality and dimensional stability.
Injection Blow Molding
Injection blow molding employs a two-step process that delivers enhanced precision compared to extrusion methods. First, a preform gets injection molded with precise dimensions, then transferred to a blow molding station where controlled inflation creates the final shape. This blow molding approach allows for more accurate neck finishes and superior dimensional control, making it preferred for technical containers and pharmaceutical applications.
Stretch Blow Molding
Stretch blow molding produces the clear PET bottles commonly used for water, soft drinks, and other beverages. This specialized blow molding process simultaneously stretches the preform longitudinally while inflating it radially. The biaxial stretching in stretch blow molding aligns polymer molecules, creating exceptional clarity, improved strength, and enhanced barrier properties that preserve product freshness.
Industrial Blow Molding
Blow molding extends far beyond consumer packaging into critical industrial applications. Large-scale blow molding operations produce automotive fuel tanks, HVAC ductwork, industrial containers, flotation devices, and playground equipment. These applications demonstrate the versatility of blow molding for creating complex hollow shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through alternative manufacturing methods.
Materials Used in Blow Molding Applications
Blow molding processes accommodate various thermoplastic materials, each chosen for specific performance characteristics. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) dominates blow molding applications for milk jugs and chemical containers due to its chemical resistance and durability. Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) serves blow molding applications requiring clarity and barrier properties, while polypropylene and PVC offer specialized properties for specific industrial and consumer applications.
Blow Molding as an Indispensable Process
Blow molding represents a highly efficient, versatile, and indispensable manufacturing process that creates the hollow plastic containers and industrial components integral to modern life. From the smallest bottles to large industrial tanks, blow molding continues shaping products that store, protect, and transport countless materials essential to contemporary society and industrial operations.